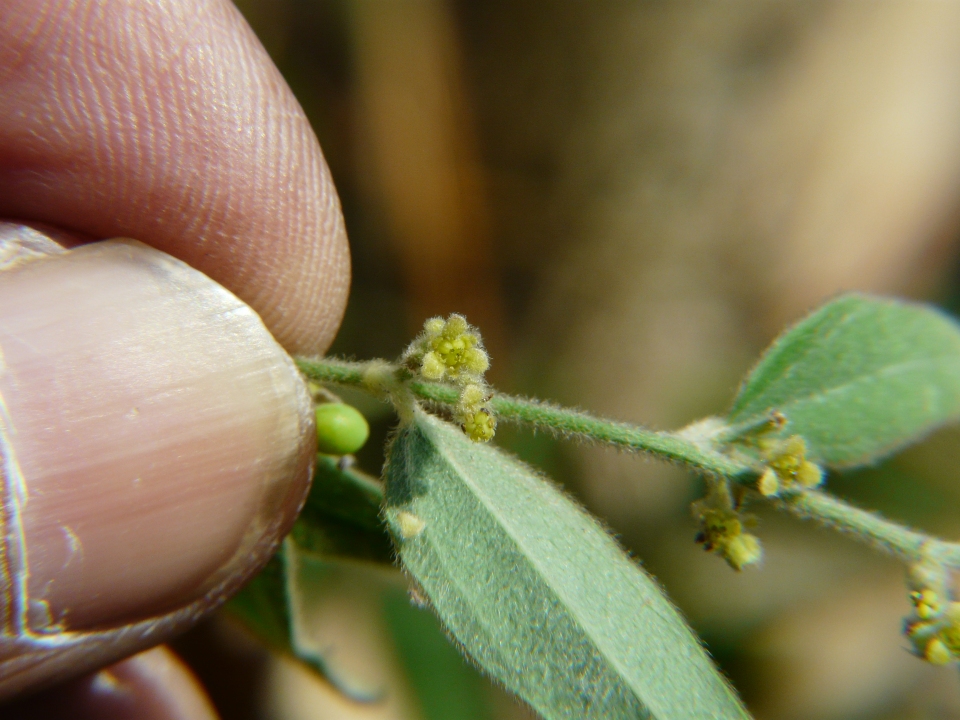

Cocculus hirsutus (L.) Diels
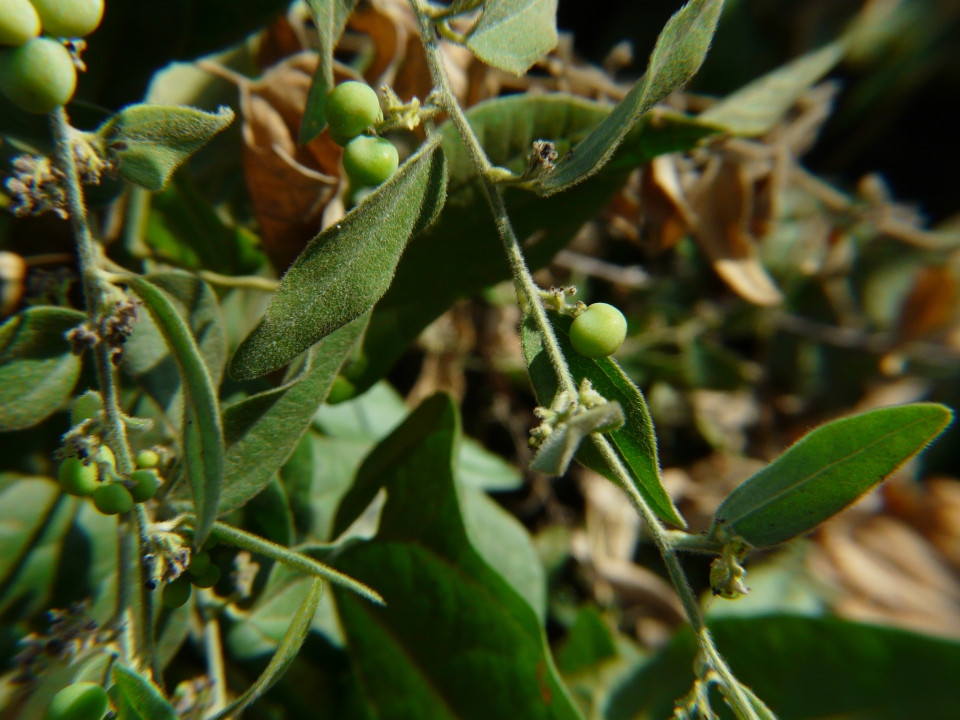

Cocculus hirsutus (L.) Diels
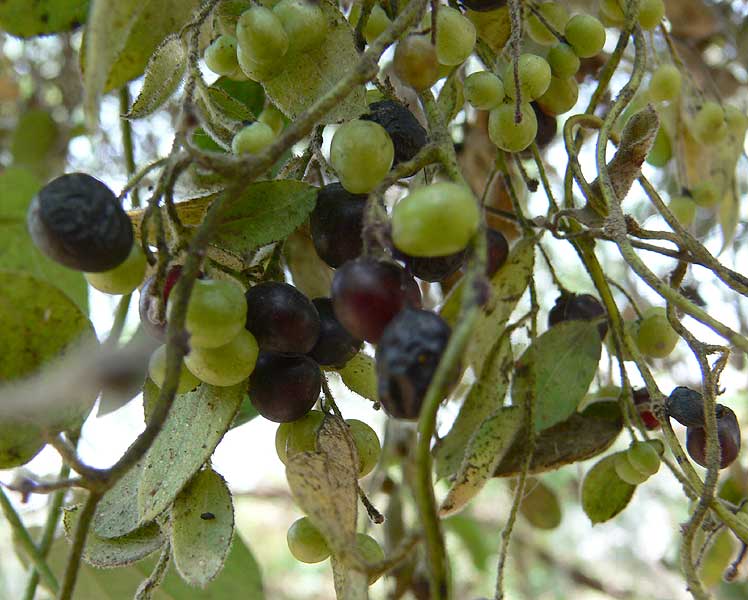

Cocculus hirsutus (L.) Diels
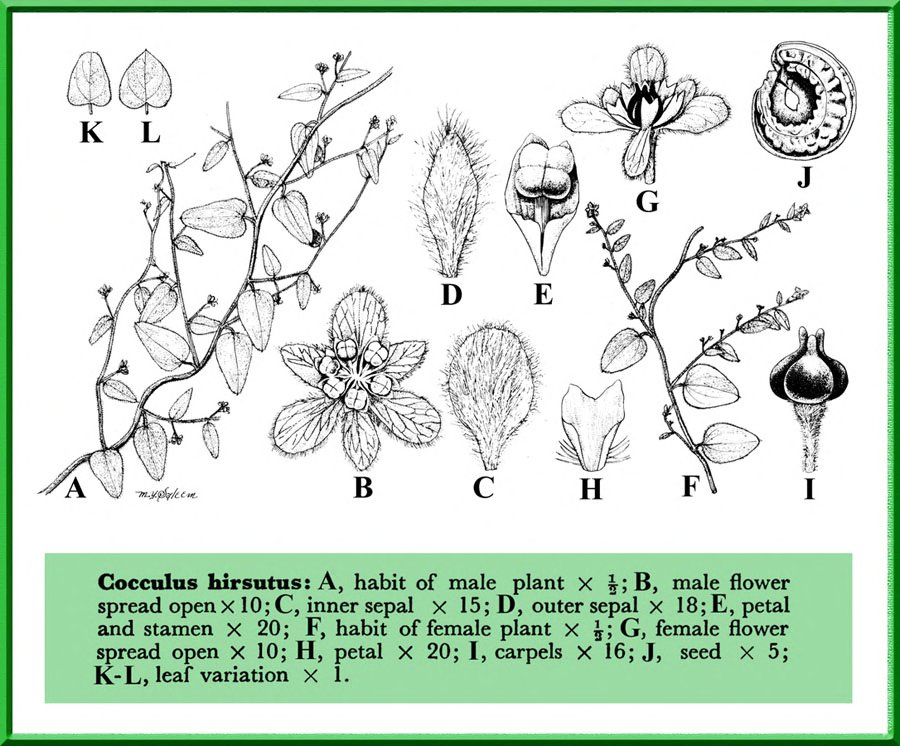
Cocculus hirsutus (L.) Diels
| Plant Category | : | Shrubs |
| Melghat's Flora's Serial No. | : | 5 |
| Synonym | : | Cebatha hirsuta (L.) Kuntze.;
Cocculus aristolochiae DC.;
Cocculus hastatus DC.;
Cocculus hirsutus (L.) W. Theobald.;
Cocculus hirsutus Diels.;
Cocculus hirsutus Druce.;
Cocculus holopeira-torrida Broun & Massey.;
Cocculus sepium Colebr.;
Cocculus villosus (Lam.) DC.;
Holopeira auriculata Miers.;
Holopeira laeviuscula Miers.;
Holopeira torrida Miers.;
Holopeira villosa Miers.;
Limacia villosa (DC.) W. Theobald.;
Menispermum hastatum Lam.;
Menispermum hirsutum L.;
Menispermum myosotis L.;
Menispermum myosotoides L.;
Menispermum myosuroides Hill.;
Menispermum villosum Lam.; |
| Plant Common Name | : | Broom Creeper, ink berry • Bengali: huyer • Hindi: farid buti • Kannada: daagadi balli, daagadi soppu, kaage maari • Konkani: vasanvel • Malayalam: paathaalagarudakkoti, paathaalamuuli • Marathi: vasanvel • Punjabi: farid buti, wallur • Oriya: musakani • Sanskrit: ambastha, dirghakanda, dirghavalli, garudi, mahamula, patalagarudi, pracina, sauparni, somavalli, sreyasi, sthapani, vanatiktaka, vatsadani, viddhakarni • Tamil: kattu-k-koti • Telugu: chipuru-tiga, dusaritiga, katlatige • Urdu: farid buti |
| Plant Family | : | Menispermaceae |
| Description | : | a climbing undershrub, often densely velvety. Leaves are 4-8 cm long, 2.5-6 cm broad, ovate or ovate-oblong, sometimes 3-5-lobed, base heart-shaped, wedge-shaped or flat, tip blunt or with a small point. Leaves are densely velvety when young, later nearly hairless. Basal nerves are 3-5. Leaf stalk is 0.5-2.5 cm long. Male flowers have sepals hairy, the outer 3, oblong-lanceshaped, 1.5-2 mm long, 0.5-0.8 mm broad, the inner 3 broadly ovate, 1.5-2.5 mm long, 1.7-2 mm broad. Petals are ovate- oblong, 0.5-1.5 mm long, 0.3-6 mm broad. Stamens are 0.7-1 mm long. Female flowers 1-3, on axillary stalks, rarely racemed. Fruit is a dark purple berry, 4-8 mm long, 4-5 mm broad, endocarp annular or ribbed with a prominent dorsal crest, perforated. The juice of the ripe fruit yields a permanent bluish-purple ink and the roots as well as the leaves are used in native medicine and as a tonic like the last species. Flowering: December-March. |
| Plant Location in Melghat | : | Common in hedges around villages |
| Medicinal Use / Activity | : | An aqueous extract of the leaves has shown diuretic and laxative properties. An infusion of the leaves is used to treat stomach-ache. A decoction is drunk to remedy female sterility. The leaf sap is used to treat nervous illnesses. The cooked leaves are eaten to treat night blindness. A jelly prepared by soaking leaves in cold water is taken to check spermatogenesis. Applied externally, the leaves are used to treat skin infections and itchy skin including eczema, rheumatism and gonorrhea. The roots are alterative, diuretic, laxative and tonic. A decoction is applied against fever, rheumatism and severe weight loss. The plants are reported to have anti-oxidant, cytotoxic, Hepatoprotective, anti-cancer, and hypotensive. It is used traditionally as alterative, laxative, demulcent, prurigo, eczema, dyspepsia tonic, diuretic, antiperiodic in fever, in malaria, joint pains and in skin diseases. |
| Plant's Phytochemicals | : | COMPOUNDS: coclaurine; cocsoline; cohirsine; cohirsinine; cohirsitinine; haiderine; hirsutine; isotrilobine; Jamtine; jamtinine; lirioresinol; shaheenine; syringaresinol; protoquericitol; D-trilobine; ACTIVE COMPOUNDS (0): |
| Plant's Current Status | : | Common |
| Plant's Cross Database Reference | : | 259142 |
| Reference | : | Dhore M. A. (1984) The flora of melghat tiger reserve
- https://www.flowersofindia.net/catalog/slides/Broom%20Creeper.html
- http://tropical.theferns.info/viewtropical.php?id=Cocculus+hirsutus
- https://indiabiodiversity.org/species/show/229234
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4971956/
- http://www.globalresearchonline.net/journalcontents/volume7issue1/Article_022.pdf |
| Reference | : | ~ J. Lenin Bapuji and S. Venkat Ratnam; "Traditional Uses of Some Medicinal Plants by tribals of Gangaraju Madugula
Mandal of Visakhapatnam District, Andhra Pradesh"; Ethnobotanical Leaflets (2009); 13: 388-98 PMID : ~ Dhore MA and Joshi PA; "Flora of Melghat Tiger Reserve"; Directorate, Project Tiger, Melghat (1988); PMID : ~ Jethva Khushboo, Bhatt Dhara, Dhru Bhavita, Patel Sonal and Zaveri Maitreyi ; "Phytopharmacognostical evaluation of leaf of Cocculus hirsutus"; Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. (2016); 38(1): 165-170 PMID : |
| Kingdom | : Plantae - Plants |
|---|---|
| Phylum | : Tracheophyta |
| Subkingdom | : Tracheobionta - Vascular plants |
| Superdivision | : Spermatophyta - Seed plants |
| Division | : Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class | : Magnoliopsida - Dicotyledons |
| Subclass | : |
| Order | : Ranunculales |
| Family | : Menispermaceae - Moonseed family |
| Genus | : Cocculus |
| Species | : Cocculus hirsutus (L.) Diels |